√ anatomy of sinuses in head 263536-Anatomy of sinuses in head
Jun 04, 21 · Sigmoid sinus (Sinus sigmoideus) The sigmoid sinus is a paired intracranial venous channel It arises from the transverse sinus at the level where the transverse sinus leaves the tentorium cerebelli The sigmoid sinus courses along the floor of the posterior cranial fossa to enter the jugular foramenAnatomy of Sinusitis The four pairs of paranasal sinuses are the maxillary, ethmoid, frontal, and sphenoid A short video demonstrating the function of the sinuses is available • The sinuses are normally air filled, lined by ciliated, pseudostratified, columnar epithelium with interspersed, goblettype, mucussecreting cellsBlood supply supratrochlear, supraorbital and anterior ethmoidal arteries;

Pin On Head And Neck Anatomy 19
Anatomy of sinuses in head
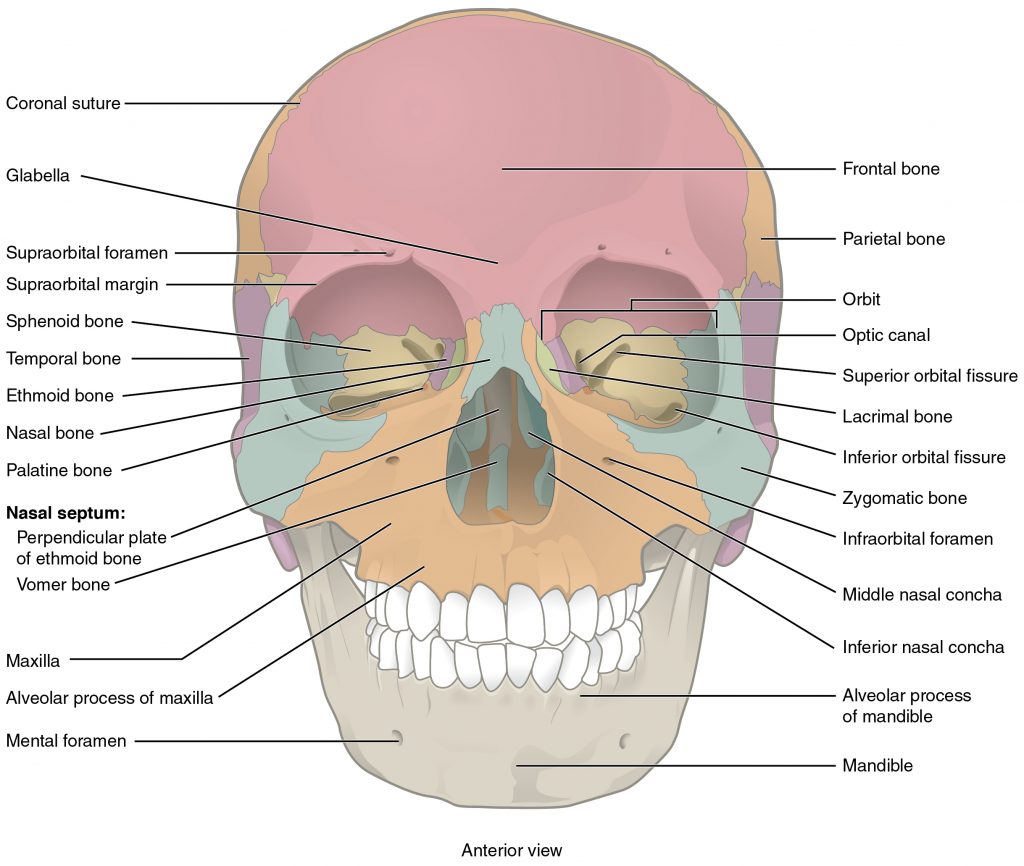
Anatomy of sinuses in head-Review questions Take Free Questions on this Article Introduction The paranasal sinuses (the hollow spaces in the skull and facial bones around the nose) are airfilled cavities within theSummary location anterior frontal bones on either side of the midline behind the brow ridges;
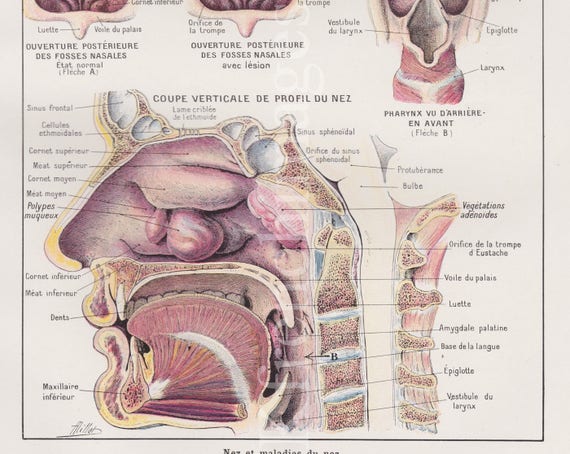



Nose Sinus Head Anatomy Plate French Vintage Original Print Etsy
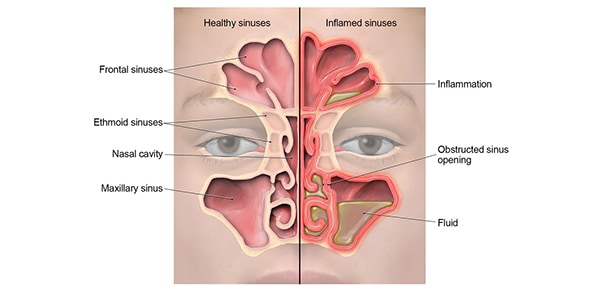
May , 13 · Each sinus is lined by a ciliated pseudostratified epithelium, interspersed with mucussecreting goblet cells The function of the paranasal sinuses is a topic of much debate Various roles have been suggested Lightening the weight of the head Supporting immune defence of the nasal cavityDrain into the superior nasal me Small compartments in the ethmoid bone;Anatomy of the Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses The nasal cavity is a large, airfilled space above and behind your nose in the middle of your face It has two openings called the nostrils, which warm and moisturize the air you breathe in
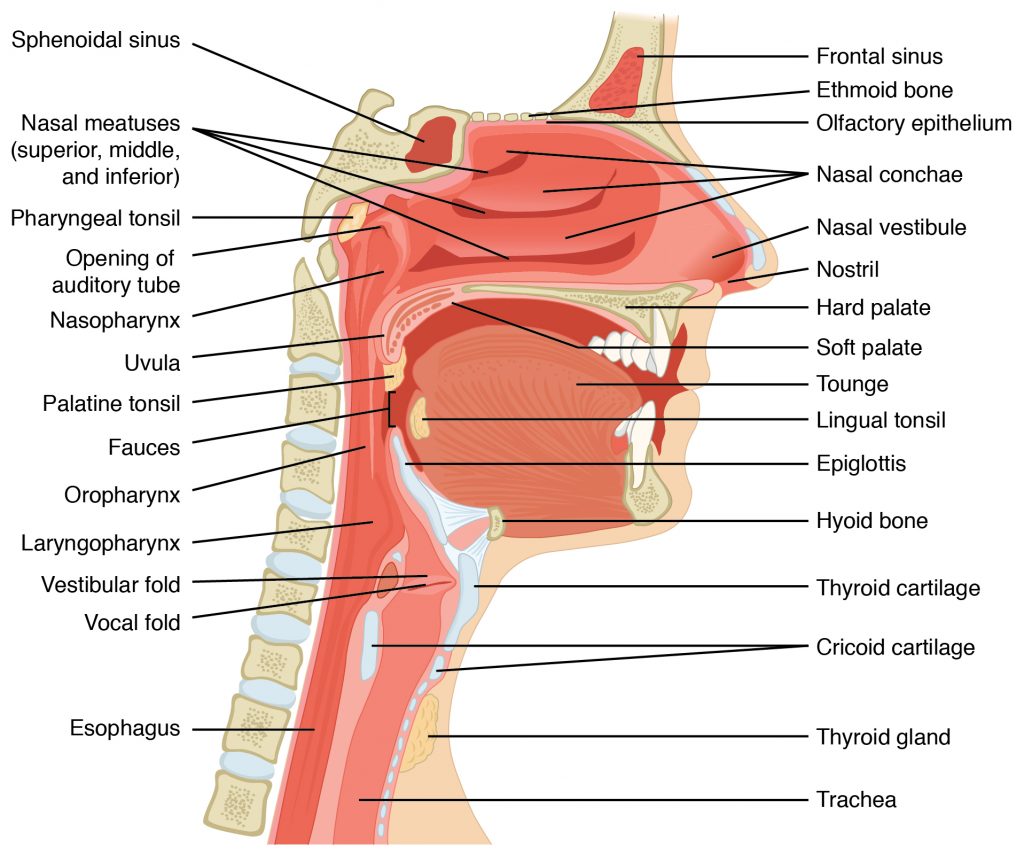
Maxillary Sinus Anatomy The maxillary sinuses were first illustrated and described by Leonardo da Vinci in 14 and later documented by the English anatomist Nathaniel Highmore in 1651 The maxillary sinus or antrum of Highmore lies within the body of the maxillary bone and is the largest and first to develop of the paranasal sinuses (FigureFigure 75 Anatomy of the Head and Neck As air is inhaled through the nose, the paranasal sinuses warm and humidify the incoming air as it moves into the pharynx The is a tubelined mucous membrane that begins at the nasal cavity and is divided into three major regions the nasopharynx, the oropharynx, and the laryngopharynxThe anatomy of the nose and paranasal sinuses can be quite complex The nose have two nasal passages that are divided by the nasal septum Both nasal passages have inferior, middle, and superior (and sometimes another called "supreme") turbinates that severe multiple purposes, including direction of airflow, filtration, and sense of smell
Anatomy of the Head & Neck Paired organs include the tonsils, parotid glands, other major salivary glands, maxillary and frontal sinuses, and the nasal cavities Specific sub sites of these organs, which are considered lateral sites, are indicated with an asterisk (*) in the code table above All other sites are considered single or nonpaired organsEthmoid sinuses Airfilled cavities lined with mucous membrane, located in the Located in the frontal bone just above the eyebrows;Uncinate attachment to skull base (medial variant) leads to Frontal Sinus draining into superior portion of ethmoidal infundibulum;




Paranasal Sinuses Wikipedia
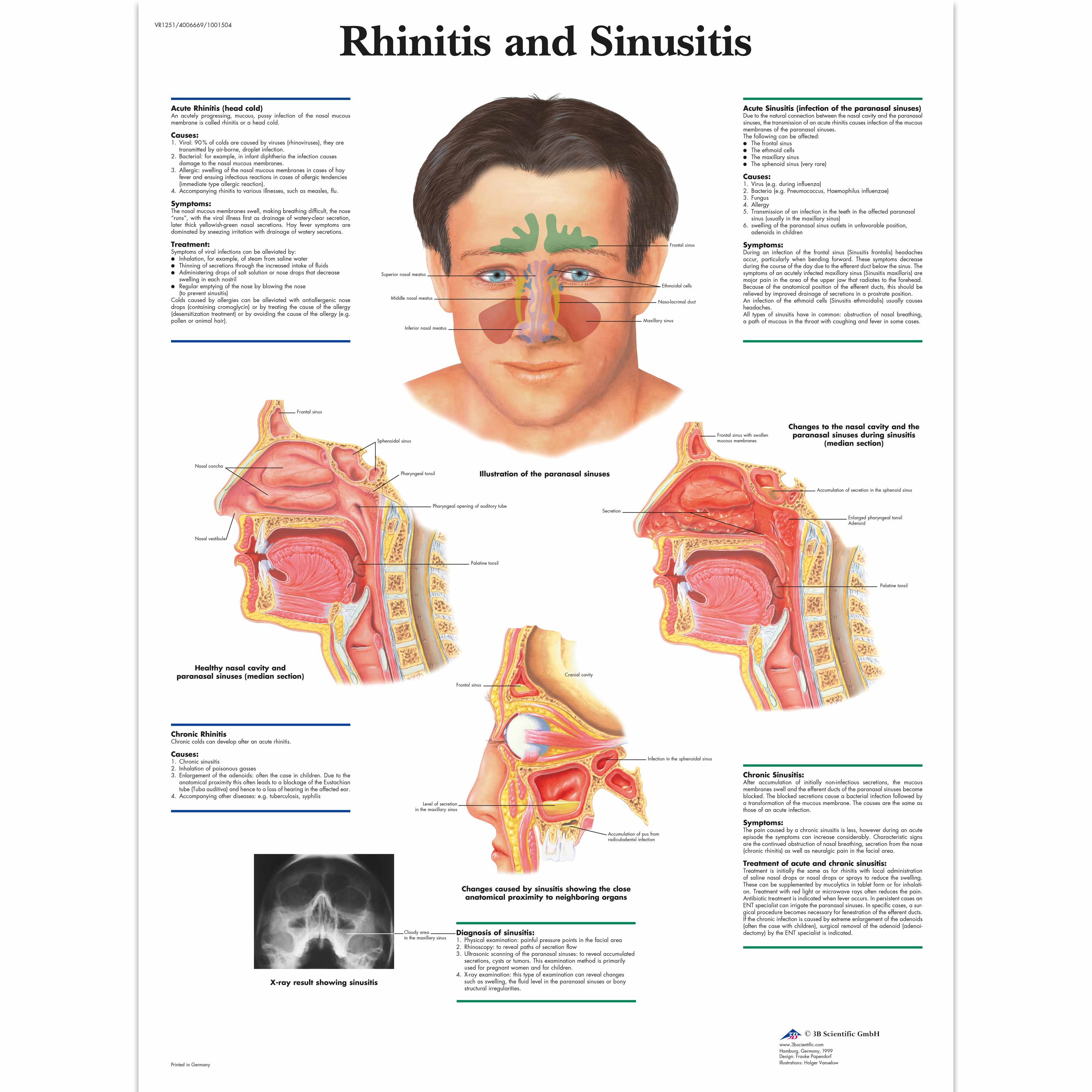



Rhinitis And Sinusitis Chart 3b Scientific Vr1251uu Ear Nose And Throat Ent Anatomy Charts And Posters
Feb 13, 21 · The carotid sinus, also known as the carotid bulb, is a neurovascular structure that appears as a dilation at the bifurcation of the common carotid artery, and the beginning of the internal carotid artery It is localized near the arterial pulse, inferior to the angle of the mandible at the level of the thyroid cartilage The carotid sinus contains baroreceptors (stretch receptors),Ninja Nerds,Join us in this video where we discuss the anatomy of the sinus skull and go into detail on the different types of sinus cavities through the useThe four paired sinuses or air cavities can be referred to as Ethmoid sinus cavities which are located between the eyes Frontal sinus cavities which can be found above the eyes (more in the forehead region) Maxillary sinus cavities are located on either side of



7 2 Head And Neck Basic Concepts Nursing Skills




Ear Paranasal Sinuses Pituitary Gland Bone Anatomy Studying Hard Face Head Png Pngegg
Nov 22, · The cavernous sinuses are a clinically important pair of dural sinuses They are located next to the lateral aspect of the body of the sphenoid bone This sinus receives blood from the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins, the middle superficial cerebral veins, and from another dural venous sinus;Mar 01, 09 · Anatomy of the paranasal sinuses The paranasal sinuses comprise four pairs of sinuses that surround the nose and drain into the nasal cavity by way of narrow channels called ostia (singular ostium) Mucus leaving the frontal (forehead) and maxillary (cheek) sinuses drains through the ethmoid sinuses (behind the bridge of the nose), so a backupBlow to the head jerks the brain tearing a vein as it heads toward a sinus over time blood accumulates, creating a space between the dura and arachnoid mater can take weeks and precipitating event may be trivial




Sinuses Picture Image On Medicinenet Com




Side View Of Mans Head With Sinus Anatomy Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock
Dec 16, · The cavernous sinus is one of the dural venous sinuses, a cavity at the base of the brain that helps drains deoxygenated blood from the brain via the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins, the superficial middle cerebral veins, the sphenoparietal sinus, and the inferior cerebral veins Anatomy, Head and Neck, External Jugular Veins 19Jul 01, 19 · Learn about the anatomical appearances of the air sinuses of the skull as seen on CT images of the brain The frontal sinuses, sphenoid sinus, ethmoid air cells and mastoid air cells have very variable appearancesSep , · It is divided in the midline by the nasal septum On each side, it is flanked by the maxillary sinuses, and roofed by the frontal, ethmoid, and sphenoid sinuses, in an anterior to posterior fashion While seemingly simple, sinonasal anatomy is composed of intricate and subdivided air passages and drainage pathways that connect the sinuses




Normal Sinus Anatomy Medical Stock Images Company



Anatomy Of Your Sinuses
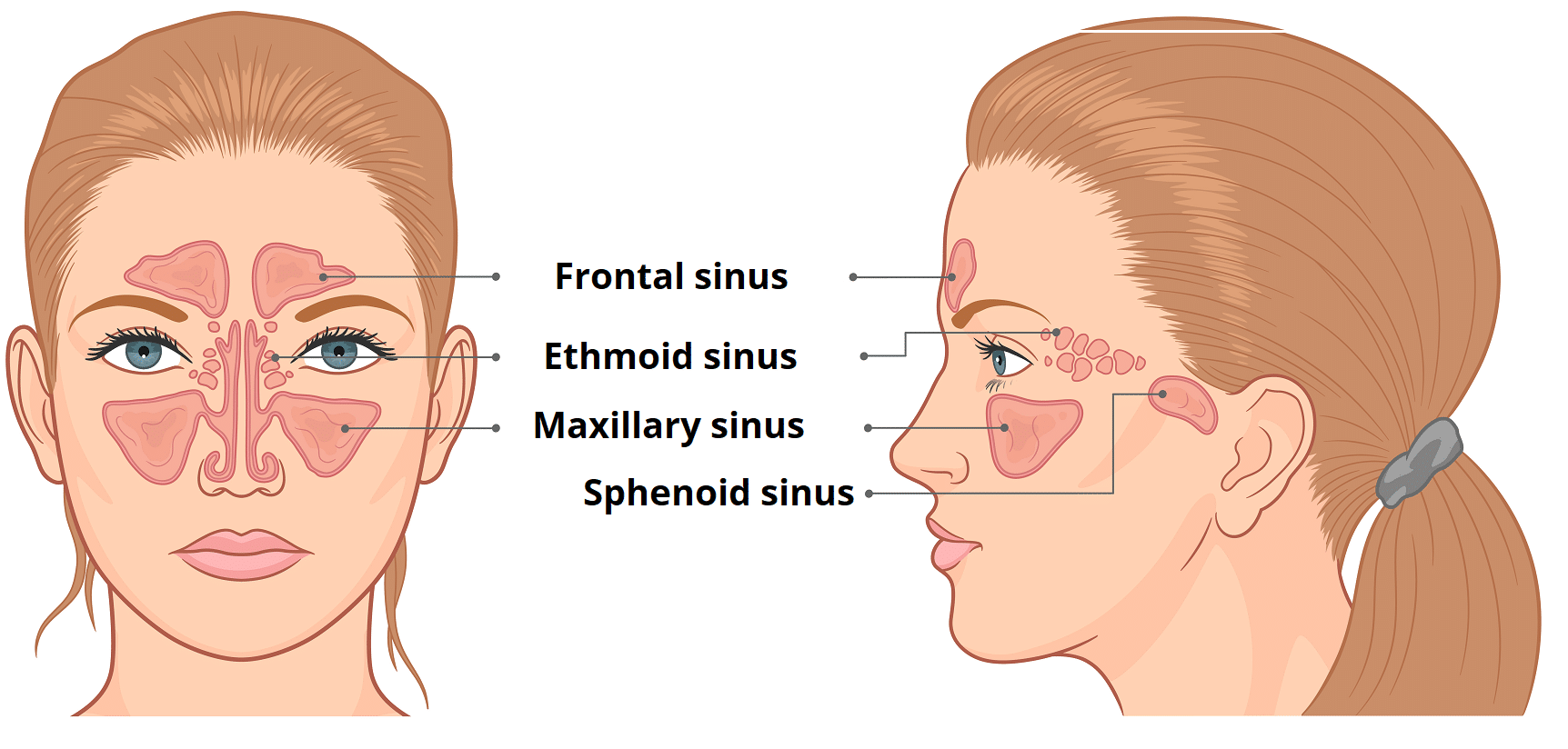
Feb 02, 15 · The frontal sinuses are in the lower center of the forehead bone, above the eyes and nasal bridge The sphenoid sinuses are behind the nasal cavity The largest sinuses, the maxillary sinuses, are in each cheekbone These structures are lined with a moist mucous membrane, and they're usually empty except for a small amount of mucusSinus Anatomy – Paranasal Sinuses Maxillary Sinuses These are found directly in behind the check Ethmoid Sinuses These are smaller pockets of air, often described as having the appearance of honeycomb Frontal Sinuses Your upper uppermost sinuses These are placed directly behind your fore headJun 17, 21 · There are two sagittal sinuses that occupy the longitudinal cerebral fissure (midline between the cerebral hemispheres) The superior sagittal sinus is the more superficial of the two sinuses It resides in the base of the falx cerebri and commences at the foramen caecum of




Open Anatomy Model Of Head With Sinuses Stock Photo Picture And Royalty Free Image Image
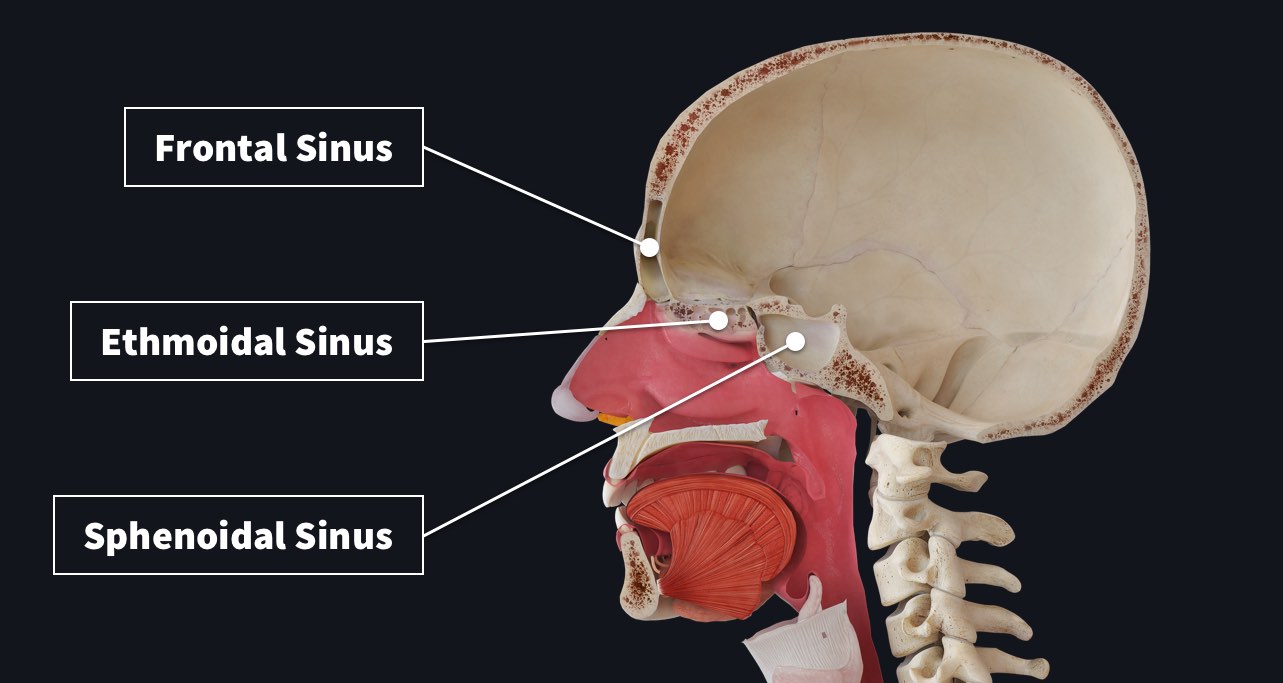



Paranasal Sinuses Complete Anatomy
Oct 31, 18 · Mucussecreting glands, responsible for making mucus cover the walls of the sinuses Sinuses are lined by mucus inside They are very crucial for confining foreign particles and bacteria that enter the body via the nostrils The sinus lining also has tiny hairs, called ciliaTeachMe Anatomy Part of the TeachMe Series The medical information on this site is provided as an information resource only, and is not to be used orUncinate attachment to middle turbinate (medial variant) causes frontal sinus to drain into the ethmoidal infundibulum




Sinus Anatomy Hd Stock Images Shutterstock




Nose Sinus Cancer Anatomy
May 28, · The ethmoid sinuses are a multiseptated series of air cells located above the nasal cavity and medial to the orbit The ethmoid sinuses are separated from the orbit by the lamina papyracea Superiorly, the ethmoid sinuses are separated from the anterior cranial fossa by the cribriform plate medially and the fovea ethmoidalis laterallyAnatomy of Paranasal Sinuses Nurul Syazwani Ramli Paranasal Sinuses The paranasal sinuses are aircontaining cavities found in the interior of the maxilla, frontal, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones They are lined with mucoperiosteum and filled with air They communicate with the nasal cavity through relatively small apertures The maxillary and ethmoid sinuses are present in aJul 31, · A sinus is defined as A channel that is not a blood or lymphatic vessel that allows for the passage of blood or lymph, such as found Anatomy, Head and Neck, Nose Sinuses Review



1




Minimally Invasive Nasal Allergy And Sinus Surgery Larian Md
Aug 19, 19 · We hope this picture Sinus Anatomy In Head And Sinusitis can help you study and research for more anatomy content please follow us and visit our website wwwanatomynotecom Anatomynotecom found Sinus Anatomy In Head And Sinusitis from plenty of anatomical pictures on the internet We think this is the most useful anatomy picture that you needDrain int Located in the sphenoid bone;Jan 27, 15 · Frontal sinuses The right and left frontal sinuses are located near the center of the forehead (frontal bone) just Maxillary sinuses These are the largest of the sinuses and are located behind the cheekbones near the maxillae, or Sphenoid sinuses The sphenoid sinuses are located in the
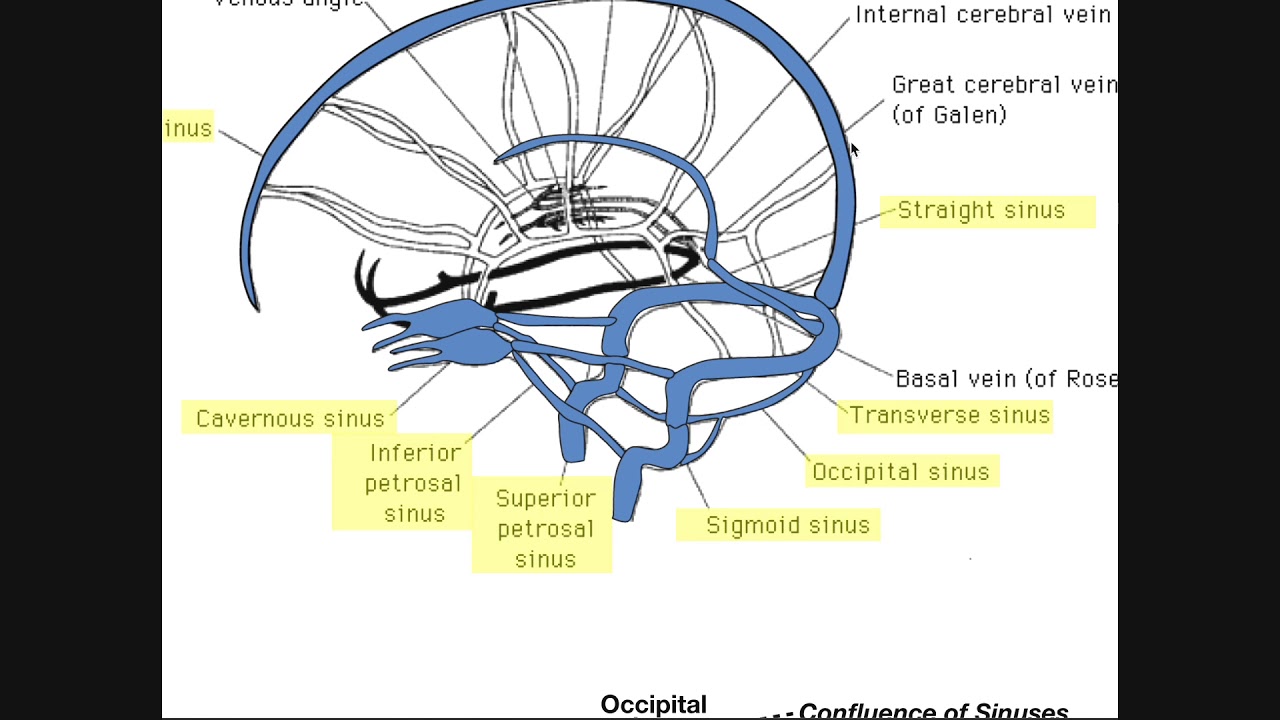



Cranial Sinuses Anatomy Ordered Flow Of Venous Blood Youtube




Startradiology
Feb 09, 21 · Anatomy of the head on a cranial CT Scan brain, bones of cranium, sinuses of the face Coronal Brain CT Vasculary territories Dural venous sinuses, Veins, Arteries Bones of cranium Axial CT Paranasal sinuses CT Cranial base , CT Foramina, Nasal cavity, Paranasal sinuses Bones of cranium Anatomy , CT Invalid inputAnatomy The nasal cavity is a potential space situated above the oral cavity and hard palate and below the skull base and intracranial compartment It is separated in the midline by the nasal septum into a right and left side The nasal septum is composed of cartilage in its front end and bone towards the back of the noseNov 03, 10 · The maxillary sinuses are the pockets near the cheeks This sinus is located in the maxilla bone under the eye, contains three recesses, and is shaped like a pyramid The frontal sinuses are over the forehead and above the eyes These are absent at birth, and in approximately 5% of the adult population




Nose Sinus Cancer Anatomy
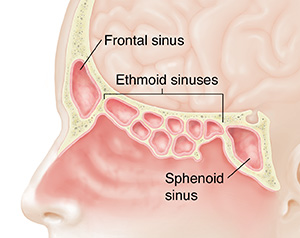



Understanding Your Sinuses
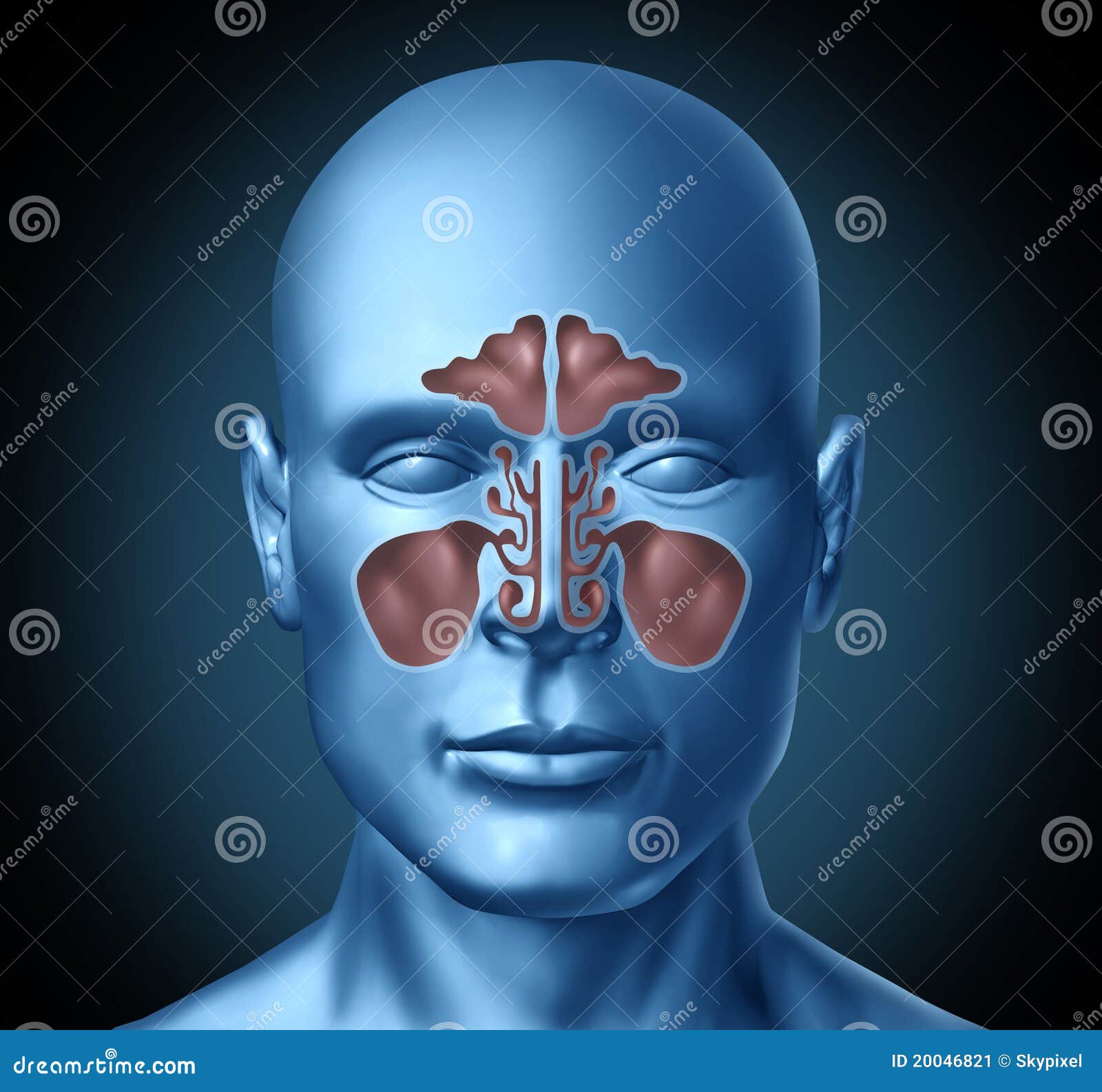
Sep 09, 09 · Picture of the Sinuses Your cheekbones hold your maxillary sinuses (the largest) The lowcenter of your forehead is where your frontal sinuses are located Between your eyes are your ethmoid sinuses In bones behind your nose are your sphenoid sinusesJun 25, 21 · This eAnatomy module contains 105 illustrations dedicated to the anatomy of the nose, the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses These fully annotated anatomical illustrations are presented as a comprehensive atlas of the nasal cavity, specially designed for medical students, medicine residents and healthcare professionalsFeb 08, 21 · All of these paranasal sinuses, except the sphenoid, communicate with the nasal cavity via ducts that drain through ostia, which empty into spaces located on the lateral wall The sphenoid sinus empties into the posterior roof Having a fundamental knowledge of the anatomy of the nasal cavity is vital in understanding its functions Respiratory



Anatomy Of The Head And Neck
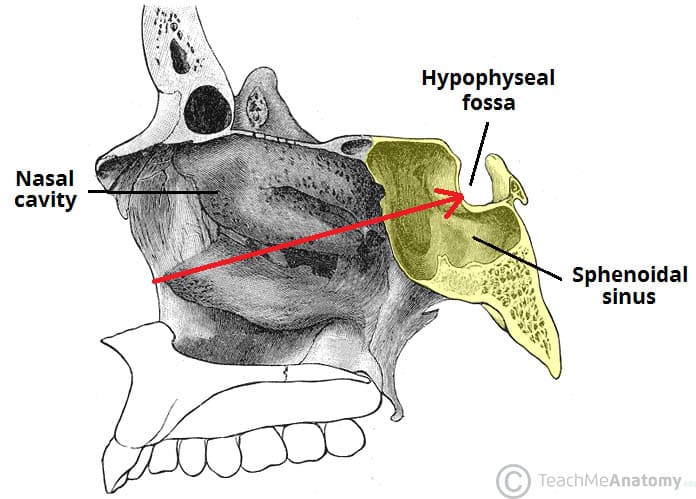



The Paranasal Sinuses Structure Function Teachmeanatomy
Sinuses are hollow, airfilled cavities that are located throughout the skull There are several sets of sinuses in the head The maxillary sinuses are behind the cheeks The ethmoid sinuses lie under the inside corners of the eyes The sphenoid sinuses are located behind the ethmoid sinuses The frontal sinuses lie behind the forehead aboveThe frontal sinuses lie above the eye and in front of the brain on each side The ethmoid sinuses are a group of smaller air cells clustered between your eyes The maxillary sinuses lie underneath each eye and the sphenoid sinuses lie in the center of your head, underneath the brain All of the sinuses have openings which communicate with theDrainage of the maxillary sinus a comparative anatomy study in humans and goats This study demonstrated that human maxillary sinuses exhibit better passive drainage through their ostia when tilted anteriorly to mimic a quadrupedal head position
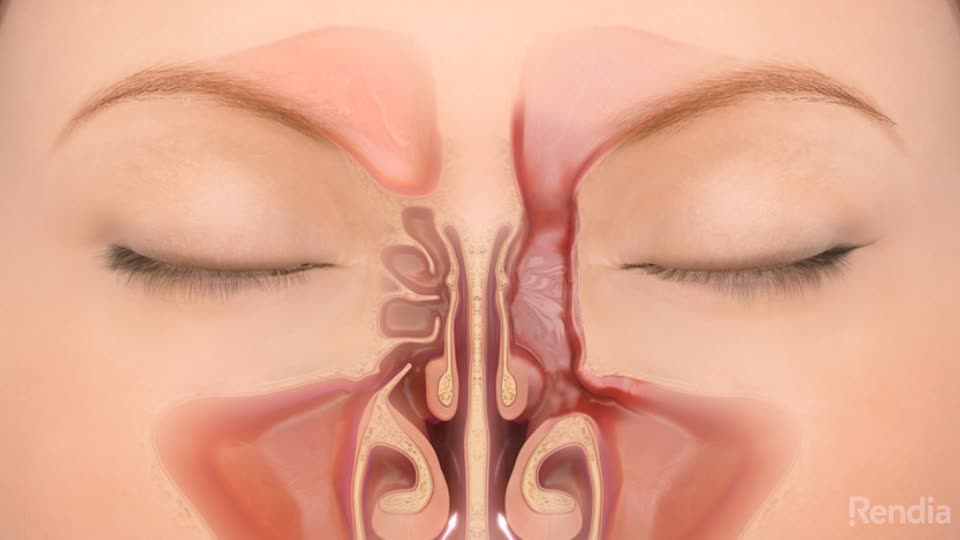



Sinus Surgery Dallas Ent
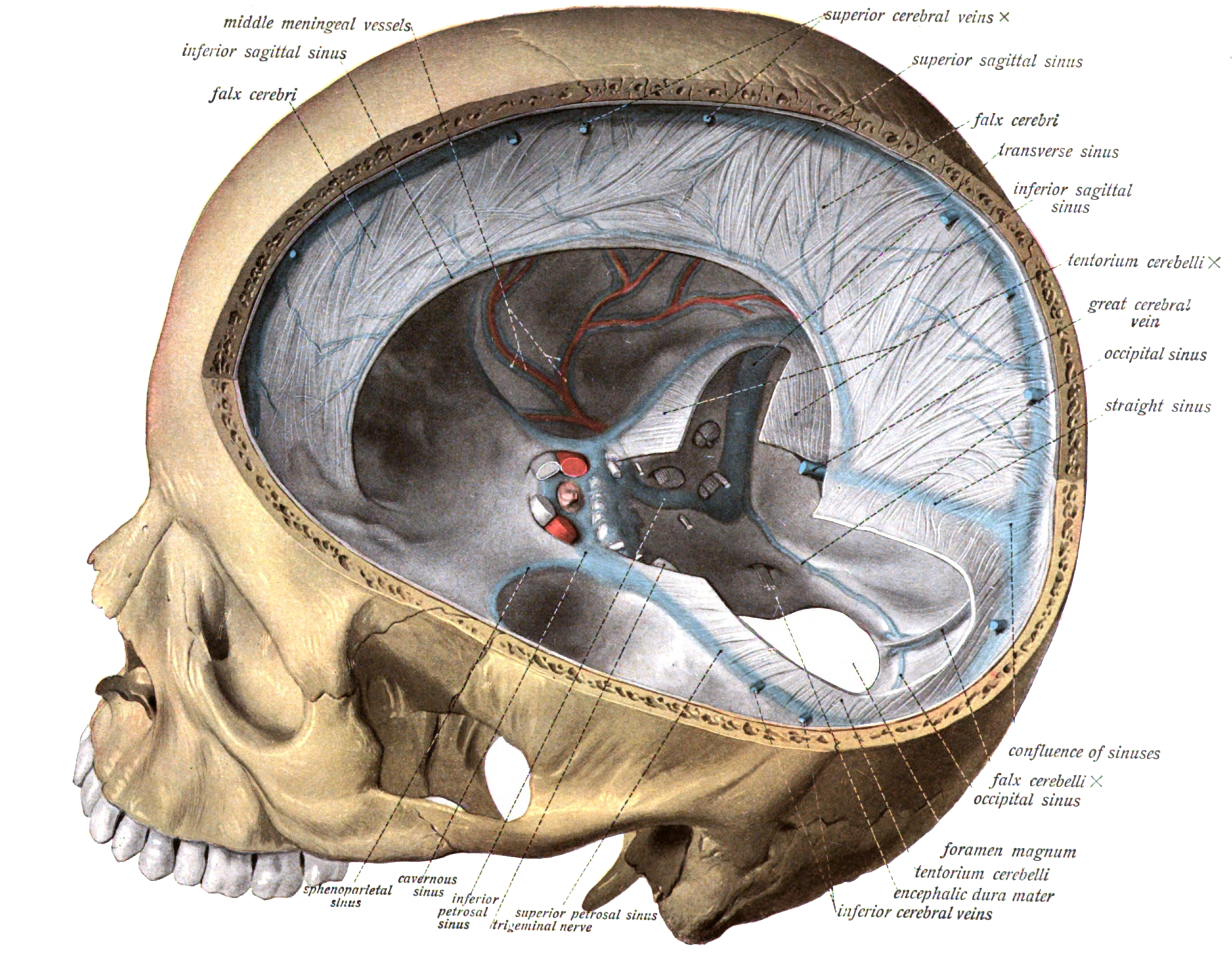



Dural Venous Sinuses Wikipedia
Mar 01, 17 · Anatomy of the paranasal sinuses, osteomeatal complex and nasal walls Maxillary sinuses (Fig 1) the maxillary sinus is pyramidal in shape with the apex in the zygomatic process of the maxilla bone and the base at the lateral wall of the nose Behind the posterior wall are the infratemporal and pterygopalatine fossaeNov 11, · Anatomy, Head and Neck, Sinus Function and Development The paranasal sinuses (the hollow spaces in the skull and facial bones around the nose) are airfilled cavities within the frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, and maxillary bones They are outgrowths from the nasal cavity All of them drain into the superior or lateral aspect of the noseAnterior and middle co Paranasal sinuses
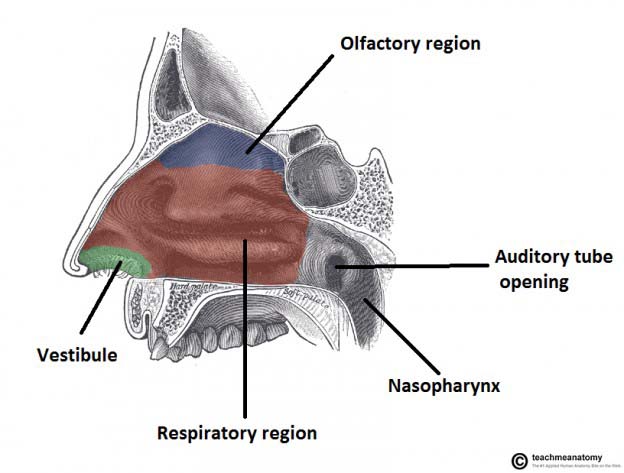



The Nose And Sinuses Teachmeanatomy




Nose And Sinuses Amboss
Mar 28, · Illustrated Anatomy Of The Head And Neck Regions Bones The Canine Head And Skull Ct Atlas Of Veterinary Clinical Cancer Of The Nasal Cavity And The Paranasal Sinuses Us 111 18 49 Off Human Head Anatomical Model Skull Anatomy Sagittal Sinus Oral Nasopharyngeal Medical Teaching Model In Medical Science From OfficeJun 19, 13 · V1 Ophthalmic nerve From Meckel's cave, it pierces the dura to enter the cavernous sinus, leaves the cranium via the superior orbital fissure and divides into nasociliary, frontal and lacrimal nervesNov 11, · Anatomy, Head and Neck, Sinus Function and Development;



Anatomy Of The Sinuses Otolaryngology Houston




Anatomy Of Your Sinus Cavities Sinussuccess
Innervation supraorbital and supratrochlear nerves Gross anatomy The frontal sinus has two chambers, one on each side, and they are almost always asymmetrical and separated by a septumSep 17, 14 · There are four pairs of paranasal sinuses, the frontal sinuses are located above the eyes, in the forehead bone The maxillary sinuses (antra of Highmore) are located in the cheekbones, under the eyes The ethmoid sinuses, also called ethmoid labyrinth are located between the eyes and the noseMay 31, 21 · Anatomy The most posterior of all the sinuses in the head, the sphenoidal sinuses are large and irregular, just like their septum, which is made by the sphenoid bone Laterally, a cavernous sinus exists which is part of the middle cranial fossa and also the carotid artery and cranial nerves III, IV, V/I, V/II and VI can be found
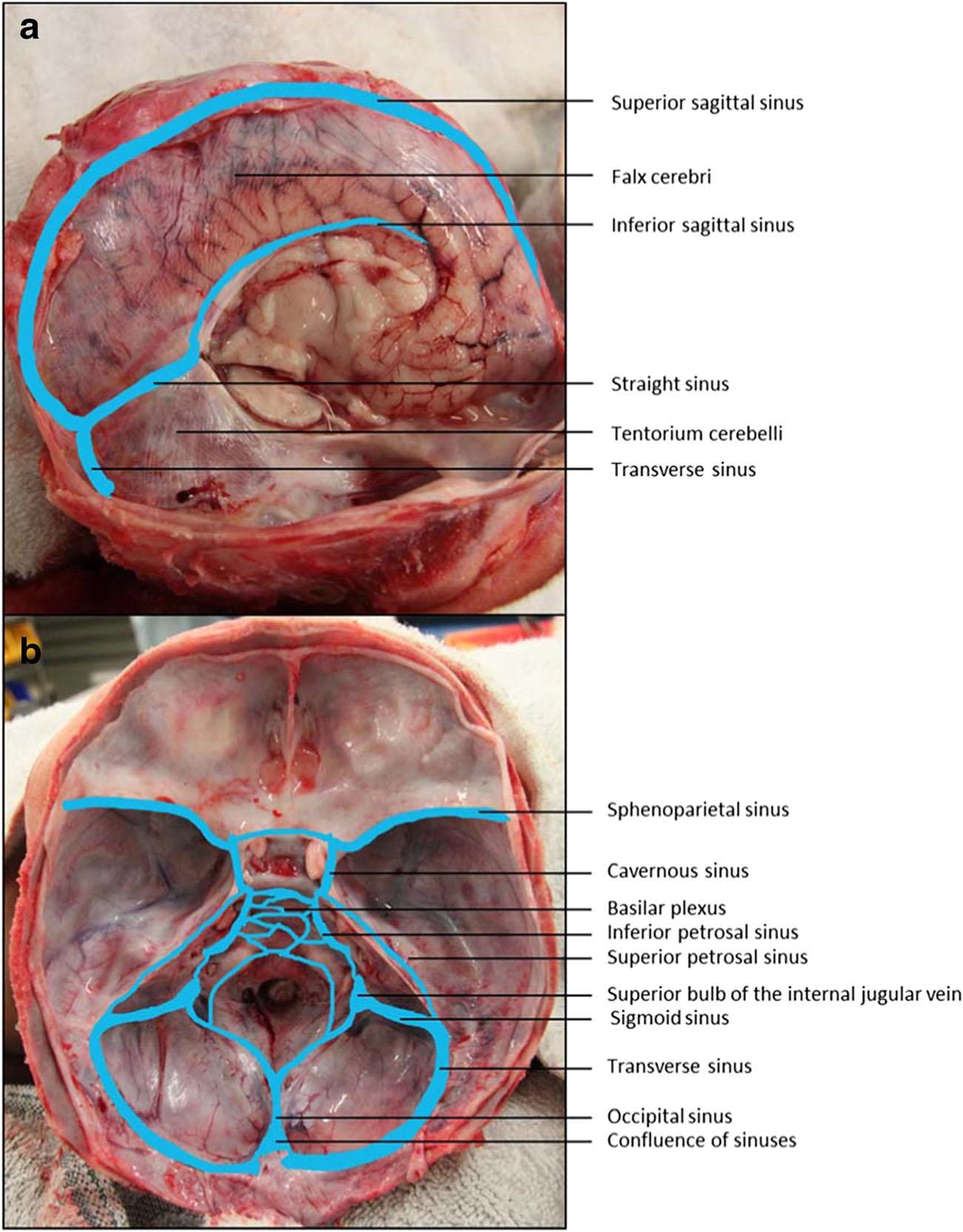



Cavernous Sinus Anatomy And Clinical Relevance Lecturio




Paranasal Sinuses Ethmoid Bone Ethmoid Sinus Nasal Cavity Nasal Cavity Anatomy Sinus Nose Png Pngwing
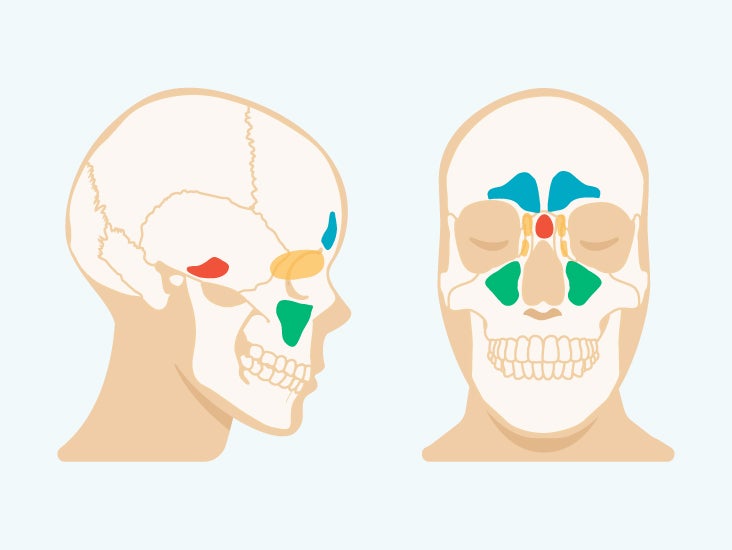



Sinus Cavities In The Head Anatomy Diagram Pictures




Anatomy Model Showing Sinus Infection Stock Illustration Illustration Of Sick Head




Paranasal Sinuses Wikipedia




Somso 3b Scientific Anatomy Models Of Head And Nose And Catawiki



The Paranasal Sinuses Structure Function Teachmeanatomy




Sinuses In Head And Throat Anatomy Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock



7 2 Head And Neck Basic Concepts Nursing Skills




Cerebral And Sinus Vein Thrombosis Circulation



Sinus Anatomy Paranasal Sinuses Sinus Pressure Points
/male-skull-in-profile-with-transparent-head-on-white-background-1092338382-d031fe3a88fa4462b0ba082a1ec64302.jpg)



Occipital Bone Anatomy Function And Treatment




Amazon Com Alkita Head Replica Features Muscular Anatomy Veins And Arteries Exposed Sinuses Brain Anatomy And Spinal Anatomy Industrial Scientific



Sinus Infection Sinusitis Antibiotic Use Cdc




Paranasal Sinus And Nasal Cavity Cancer Treatment Adult Pdq Pdq Cancer Information Summaries Ncbi Bookshelf




Sinusitis Uci Head And Neck Surgery Uci Ent Doctors Otolaryngologists




9 Nasal Cavity Ideas Nasal Cavity Anatomy Sinus Cavities




Human Head Anatomy Illustration Stock Image C050 6954 Science Photo Library




Model Of Frontal Section Of Human Head Paranasal Sinuses Includes Gtsimulators Com



Sinus Cavity Human Head Stock Illustrations 150 Sinus Cavity Human Head Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Pin On Head And Neck Anatomy 19




Sinus Anatomy In Head And Sinusitis
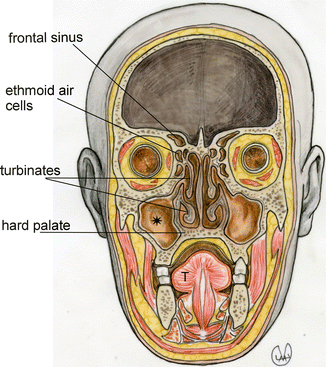



Head And Neck Radiology Key
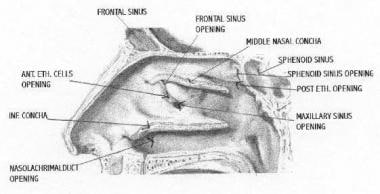



Acute Sinusitis Practice Essentials Background Anatomy
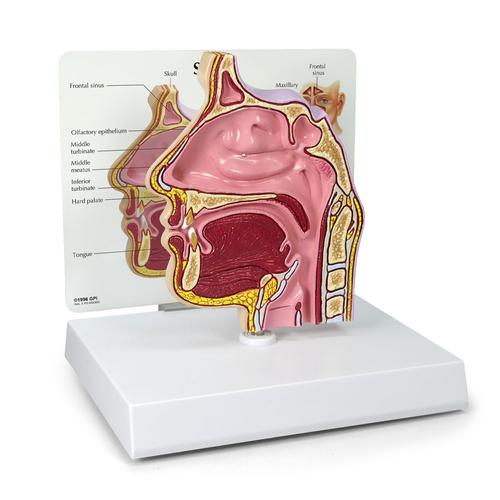



Sinus Cross Section 2850 Anatomical Models Anatomy Teaching Models Cranial Models Head Models




Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinus Cancer Miami Cancer Institute Baptist Health South Florida




Paranasal Sinuses Head X Rays Stock Image C040 3063 Science Photo Library




Nose Sinus Head Anatomy Plate French Vintage Original Print Etsy




What To Do About Sinusitis Harvard Health
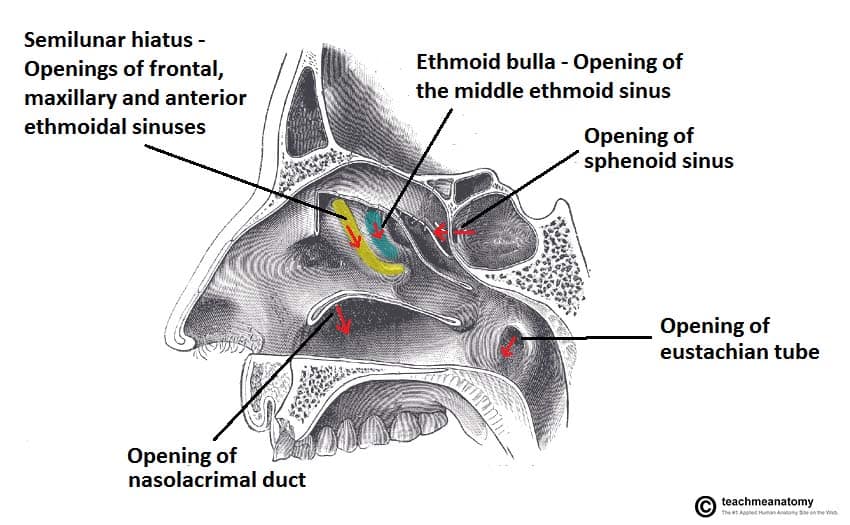



The Paranasal Sinuses Structure Function Teachmeanatomy



Equine Head Nasal Sinus Anatomy Plastination Anatomy Embedding




Nose And Paranasal Sinus
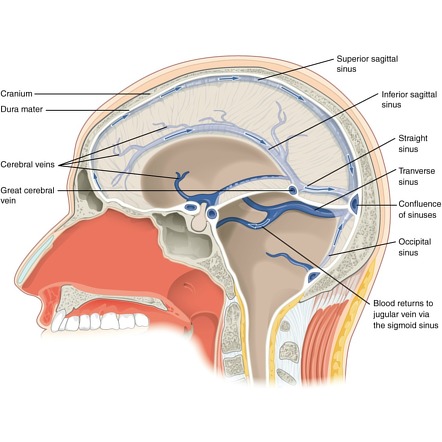



Dural Venous Sinuses Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
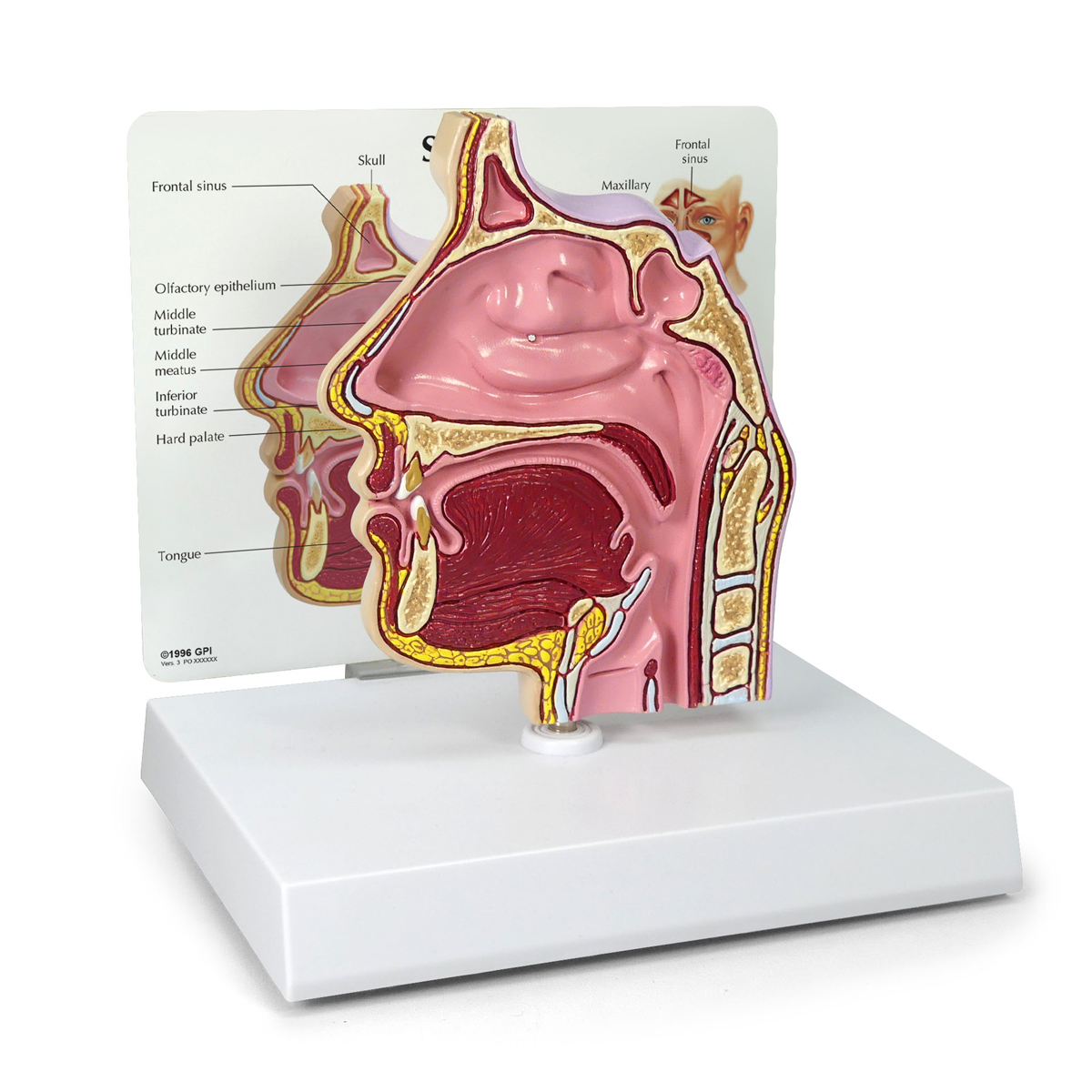



Sinus Cross Section 2850 Anatomical Models Anatomy Teaching Models Cranial Models Head Models



Nasal Anatomy Uc Irvine Medical Center
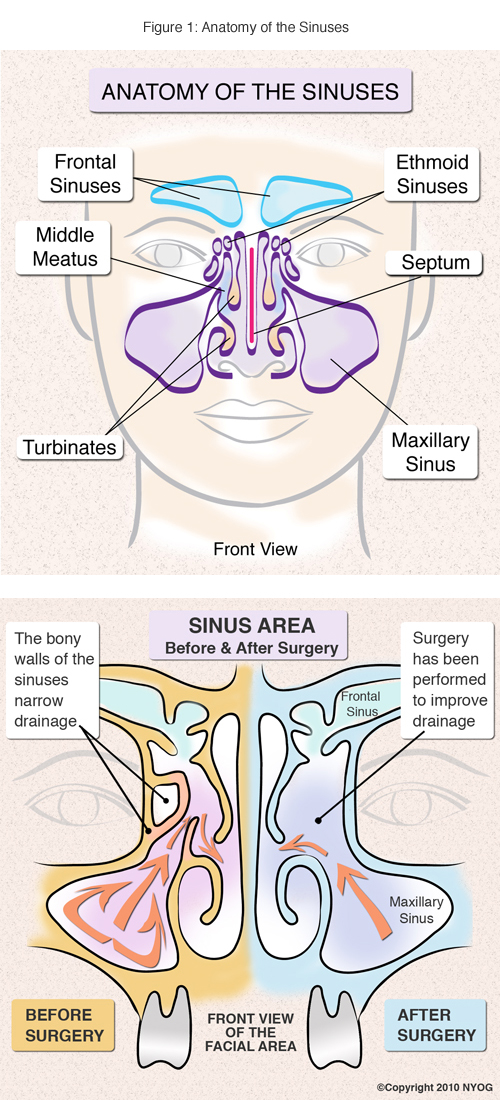



Sinus Anatomy Check Out This Helpful Diagram Ny Sinus Center




Sinus Anatomy Hd Stock Images Shutterstock




Head Sinus Fill In Diagram Quizlet
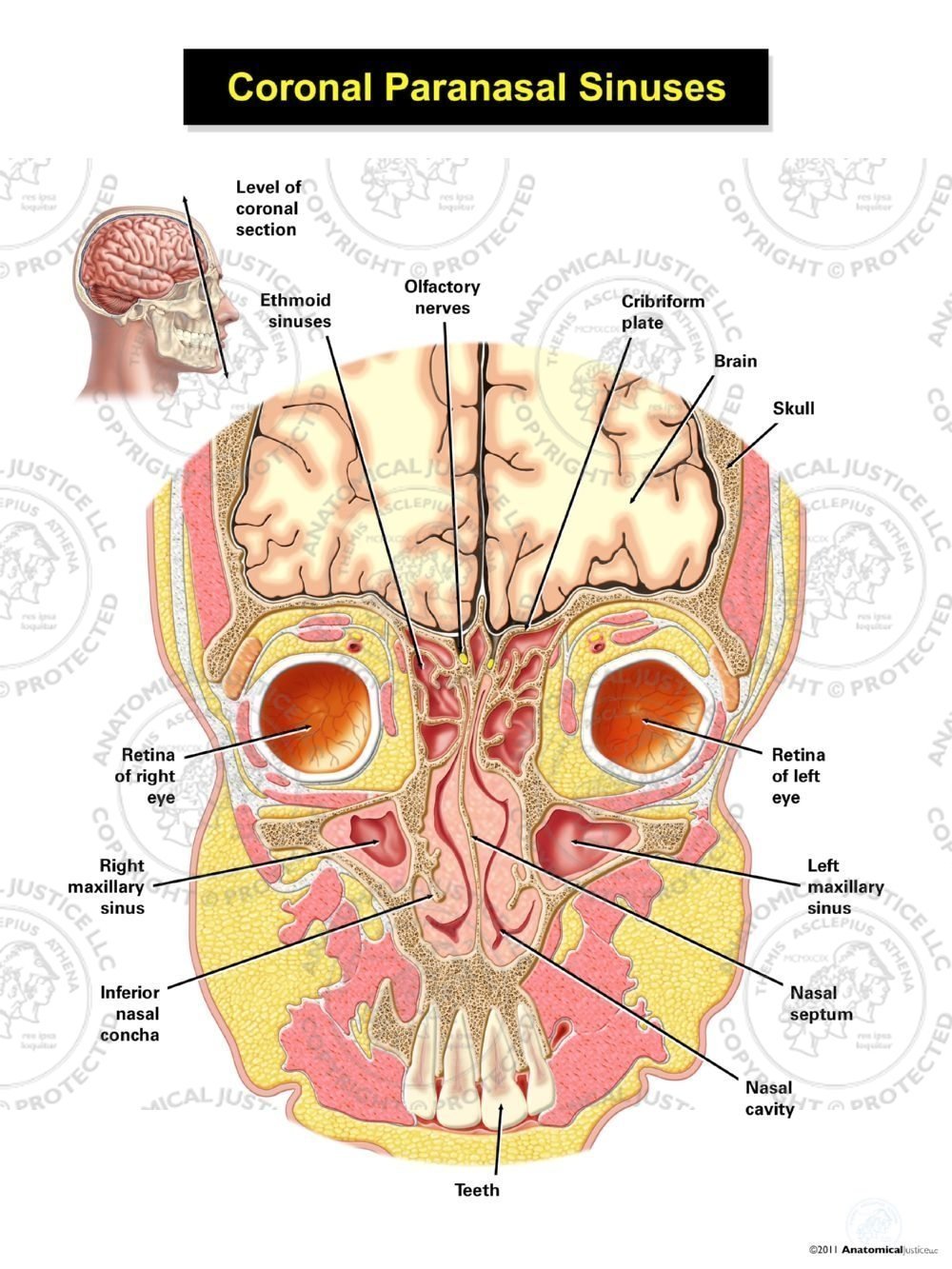



Coronal Paranasal Sinuses




Anatomy Head And Neck Sinus Function And Development Article
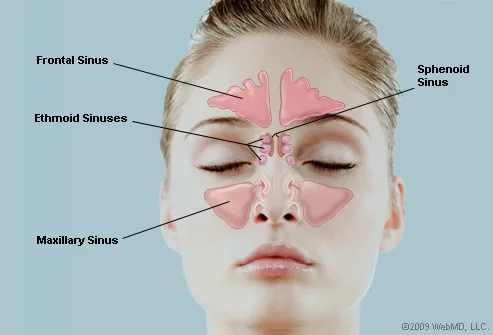



What Are The Sinuses Pictures Of Nasal Cavities
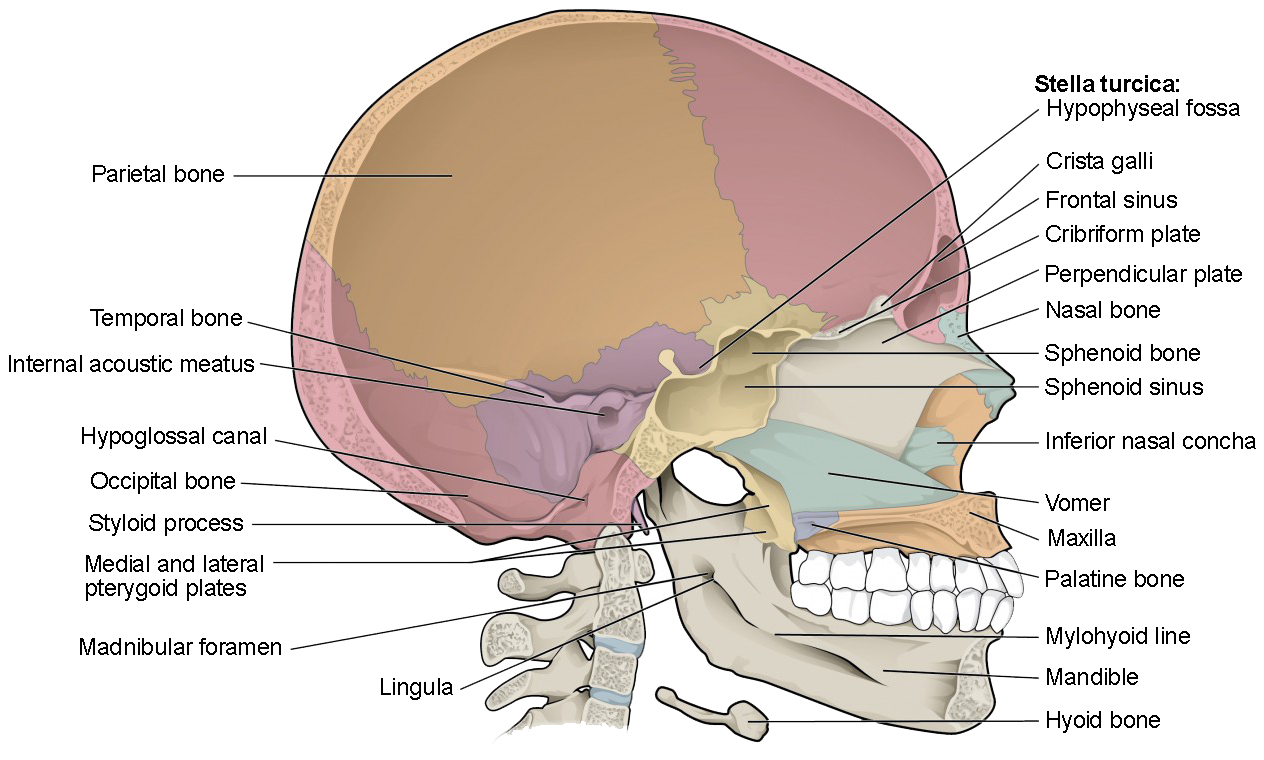



The Skull Anatomy And Physiology I




Cross Sectional Anatomy Panel A And Mr Image Panel B Of Horse Head Download Scientific Diagram



1
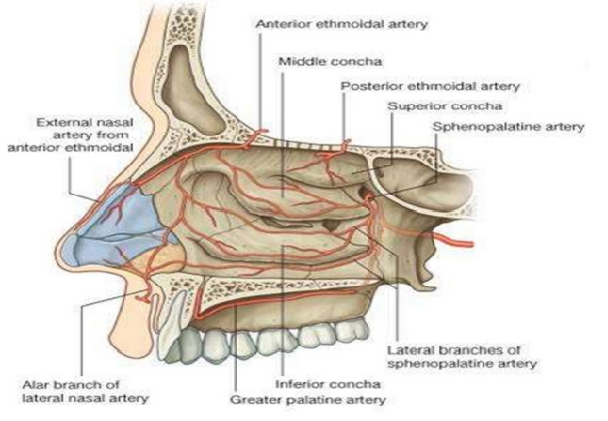



Anatomy Head And Neck Nose Sinuses Article




Nasopharynx Anatomy Britannica




Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




Brain And Face Ct Interactive Anatomy Atlas
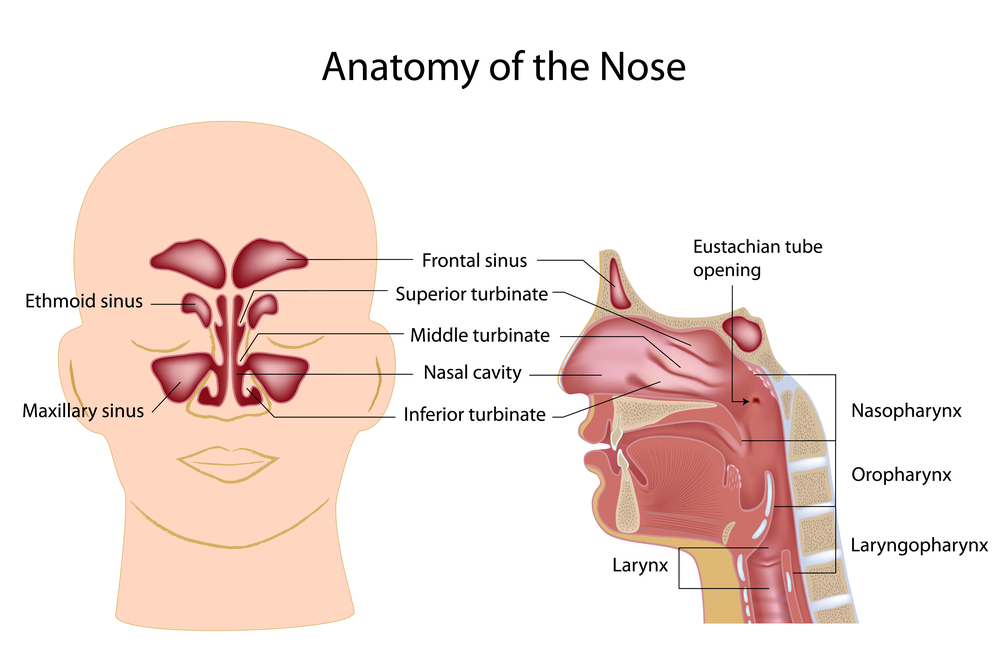



Bubbles In Sinus Area Popping Noises Sinus Infection Symptoms




Pin On Ent Head Neck Surgery




Diagrammatic Representation Of The Anatomy Of The Sinuses Within The Download Scientific Diagram
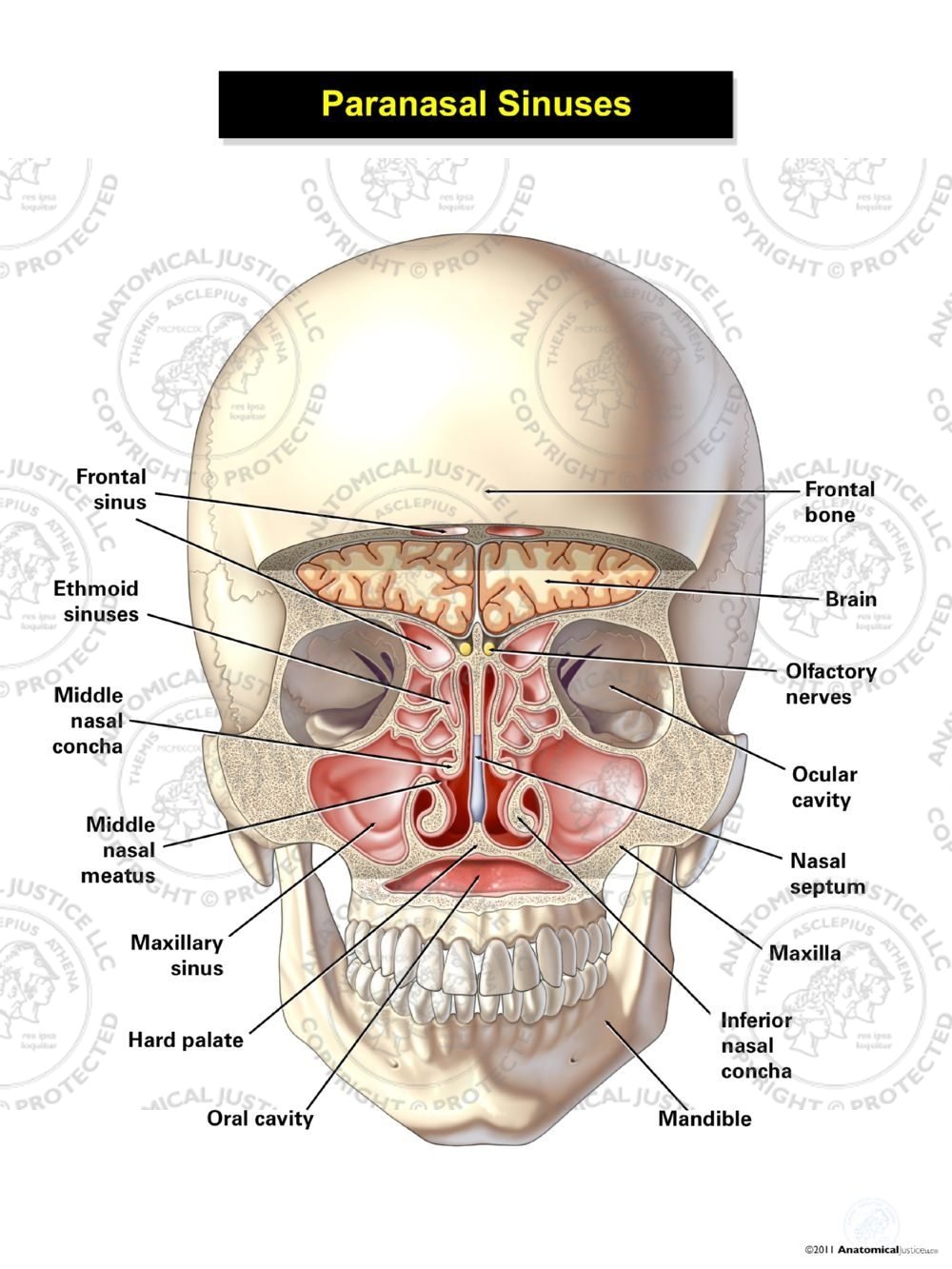



Paranasal Sinuses Illustration Anatomical Justice
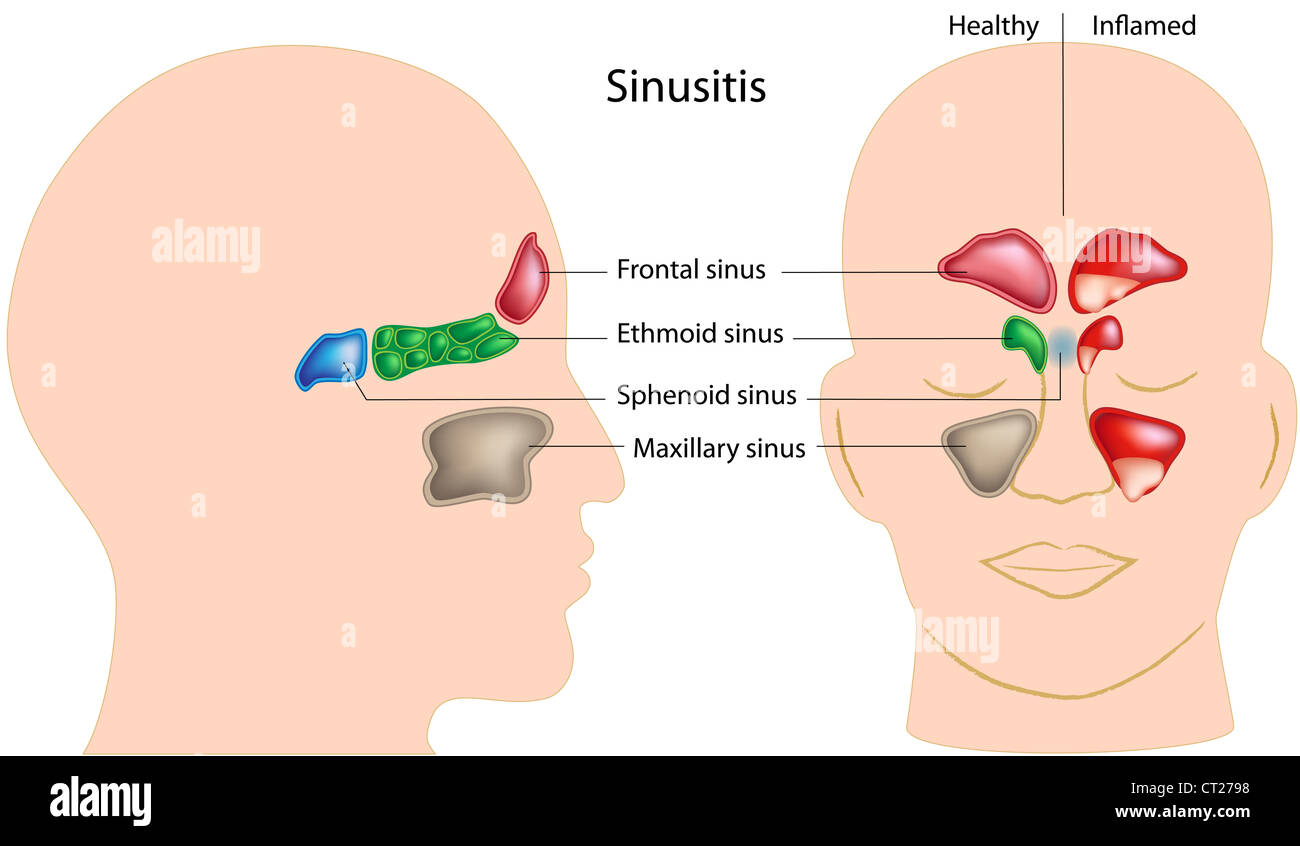



Sinuses Of Human Head And Sinusitis Stock Photo Alamy
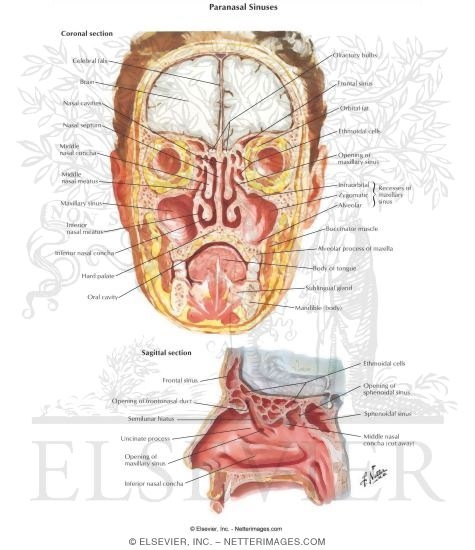



Paranasal Sinuses Coronal And Sagittal Sections
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13677/8iVwiSwwNxvJhpSQELoQ_Sinus_sagittalis_superior_02.png)



Superior Sagittal Sinus Anatomy Tributaries Drainage Kenhub
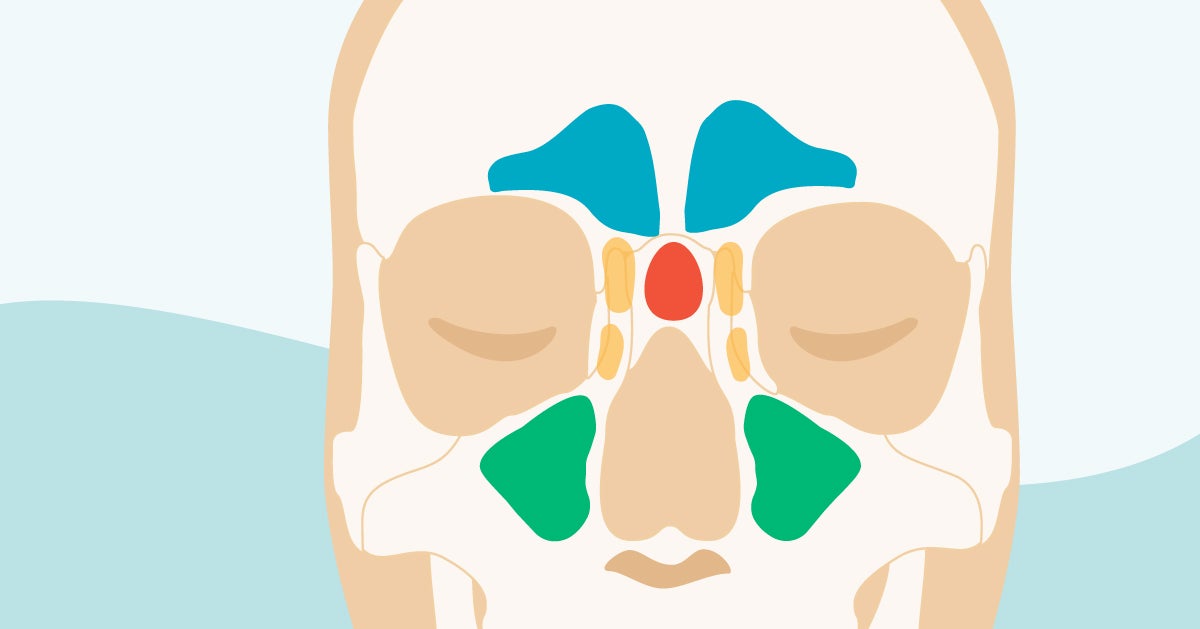



Sinus Cavities In The Head Anatomy Diagram Pictures




Patient Resource Publishing Immunotherapy Sinus And Nasal




9 Nasal Cavity Ideas Nasal Cavity Anatomy Sinus Cavities



1




Sinus Infection Sinusitis Symptoms Treatment



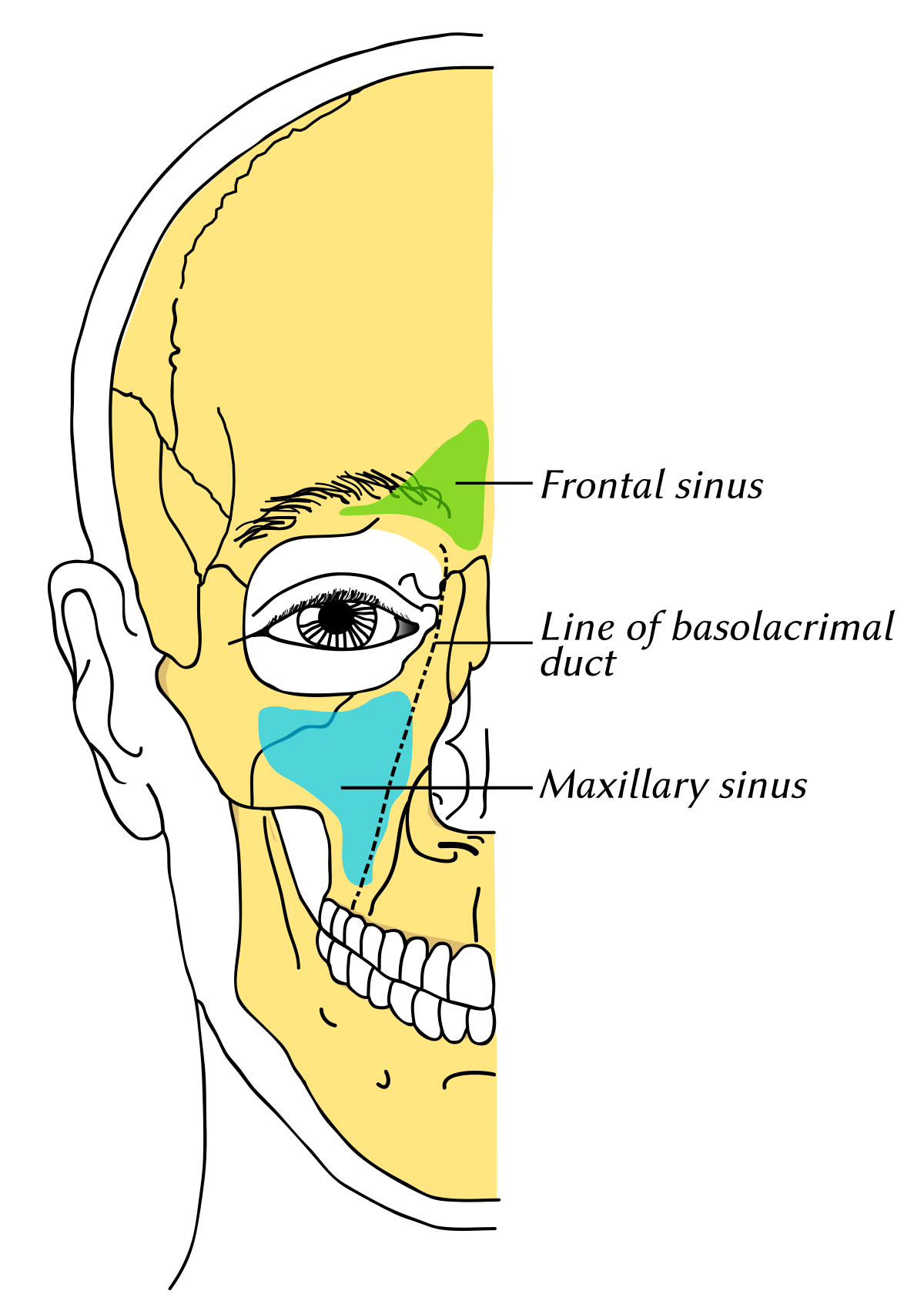
Anatomy Of Sinuses In Head Anatomy Drawing Diagram



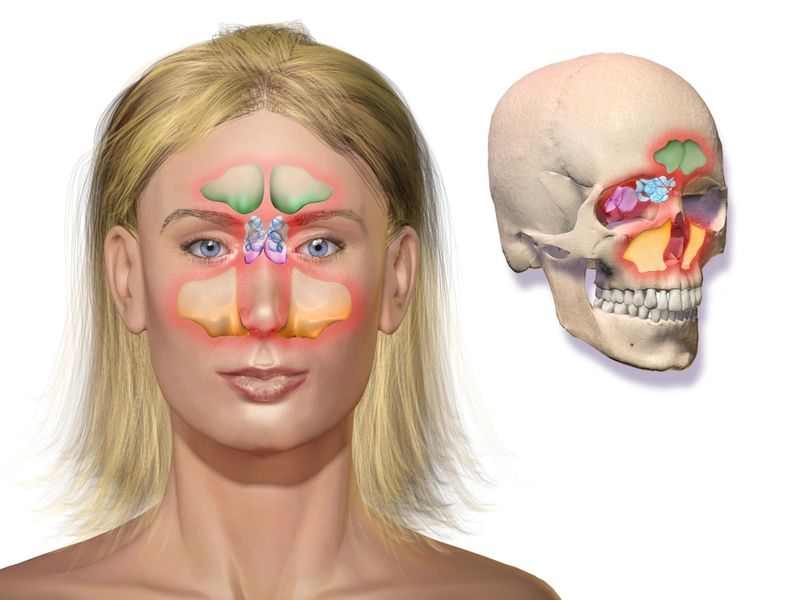
Maxillary Sinus Wikipedia



Sinusitis Reflexology And Indian Head Massage Could Help




Doctors May Have Found Secretive New Organs In The Center Of Your Head The New York Times
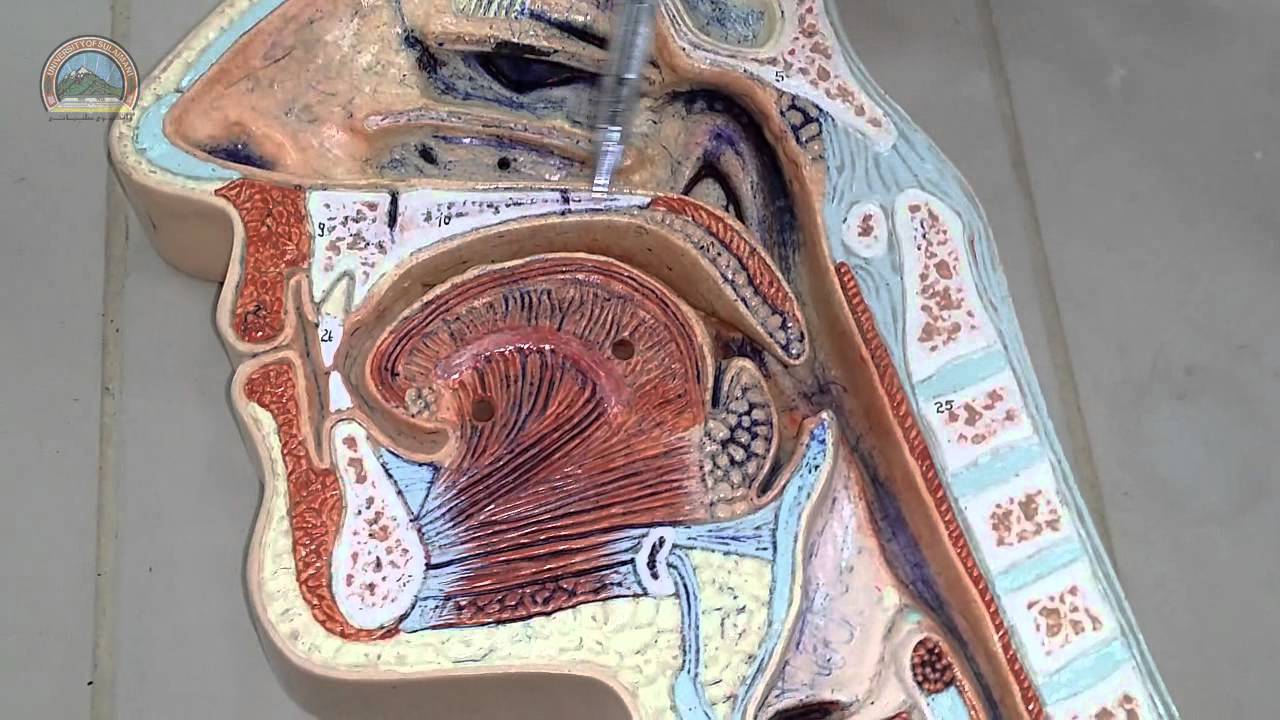



Anatomy Of Nasal Cavity Head Sagittal Section Updated Youtube
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/the-paranasal-sinuses/972PC0nYOzlz7wqSgLmNA_sinus_frontalis_large_u9Vfozc0uUoMtc6KtIaUfw.png)



Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub




Sinus Center Anatomy Otolaryngology Head Neck Surgery Ohns Stanford Medicine
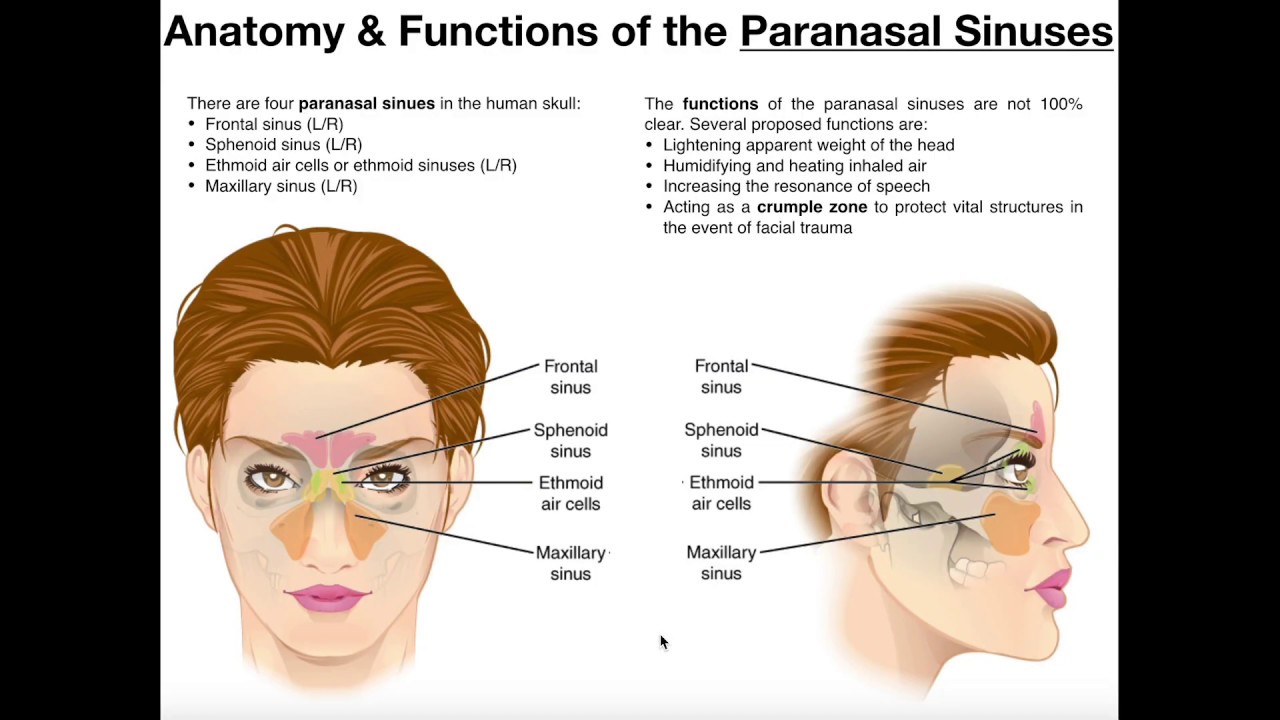



Anatomy And Functions Of The Paranasal Sinuses Youtube




Human Head Neck Skull Anatomy Medical Anatomical Chart Educationalmodel Com Amazon Com Books




Nose Sinus Cancer Anatomy




Sinus Pressure And Pain Specialist Spokane Washington Columbia Surgical Specialists
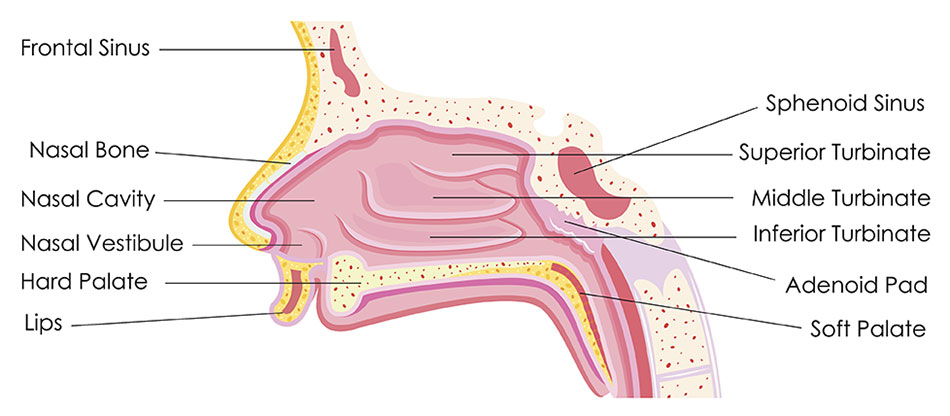



Sinus Nasal And Skull Base Cancer Of Wisconsin




Maxillary Sinus Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




Nose And Sinuses Amboss




Paranasal Sinus High Res Illustrations Getty Images




Pin On Topography Of The Skull



1
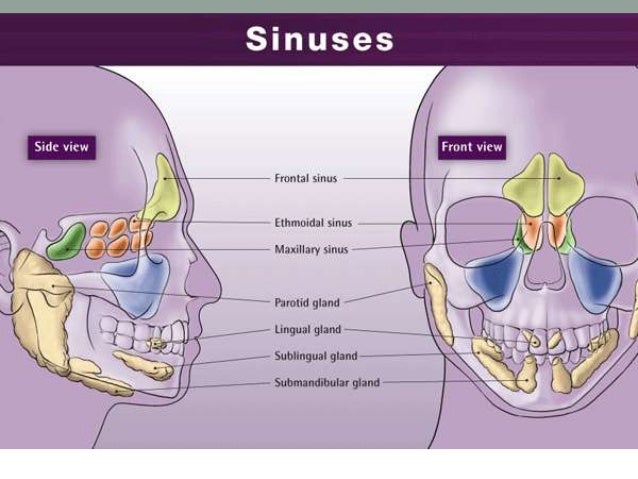



Head And Neck Anatomy


コメント
コメントを投稿